How to enable and configure Web Content Filtering within Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
So here is the situation. You access Microsoft Defender 365 Portal to enable Web Content Filtering, only to find out it is missing. What do you do?
To turn on the preview experience setting,
1. Navigate to Microsoft 365 Defender Portal > Settings > Endpoints > Advanced features > Preview features.
2. Toggle the setting between On and Off and select Save preferences.
Refresh the page and you should see Web Content Filtering listing under Endpoint > Rules.
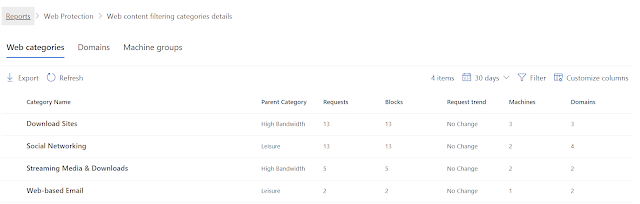
Web content filtering is part of Web protection capabilities in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. It enables your organization to track and regulate access to websites based on their content categories.
You can configure policies across your device groups to block certain categories. Blocking a category prevents users from accessing URLs associated with the category. For any category that's not blocked, the URLs are automatically audited and your users can access the URLs without disruption. The users will see a block notification if an element on the page they're viewing is making calls to a blocked resource.
There are some Pre-requisites that you need to consider before using this feature.
1. Windows 10 Enterprise E5, Microsoft 365 E5, Microsoft 365 E5 Security, Microsoft 365 E3 + Microsoft 365 E5 Security add-on, or the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint standalone license.
2. Access to Microsoft 365 Defender portal (https://security.microsoft.com).
3. Devices running Windows 10 Anniversary Update (version 1607) or later with the latest MoCAMP update.
4. Windows Defender SmartScreen and Network Protection enabled.
I will be covering some of the pre-requisites in another post so for now I will dive right into configuring Web Content Filtering rule.
1. Sign into https://security.microsoft.com
2. Click on Settings and Endpoints
3. Navigate to Web Content Filtering and Add item by the name Web content Baseline Policy (or whatever you wish to call it.)
4. Select the following categories.
|
Categories |
Recommended to be blocked |
|
Adult content |
|
|
Cults |
√ |
|
Gambling |
√ |
|
Nudity |
√ |
|
Pornography/Sexually explicit |
√ |
|
Sex education |
√ |
|
Tasteless |
√ |
|
Violence |
√ |
|
High bandwidth |
|
|
Download sites |
√ |
|
Image sharing |
|
|
Peer-to-peer |
√ |
|
Streaming media & downloads |
√ |
|
Legal liability |
|
|
Child abuse images |
√ |
|
Criminal activity |
√ |
|
Hacking |
√ |
|
Hate & intolerance |
√ |
|
Illegal drug |
√ |
|
Illegal software |
√ |
|
School cheating |
√ |
|
Self-harm |
√ |
|
Weapons |
√ |
|
Leisure |
|
|
Chat |
√ |
|
Games |
√ |
|
Instant messaging |
√ |
|
Professional networking |
|
|
Social networking |
√ |
|
Web-based email |
√ |
|
Uncategorized |
|
|
Newly registered domains |
|
|
Parked domains |
|
5. Assign a Device group. I already created a group containing all Windows 10 Devices and you can do the same. It is important to scope the rule as devices in the selected groups will be prevented from accessing websites in the selected categories. Once done, the rule will show up and you can access it to verify for the settings.
Once your Web Content filtering rules are in place, you can head over to Reports in Defender 365 Portal and access the Web Protection Card to see the rules in action.
Web Content Filtering is still in public preview so there are some known issues and limitations. However, if you have invested in an M365 E5 license or equivalent that contains the Defender for Endpoint service, then you can use the feature right out of the box without feeling the need to invest any further in implementing similar Web Content Filtering capabilities.









Comments
Post a Comment